Social Fills Gap In Business Process Spectrum
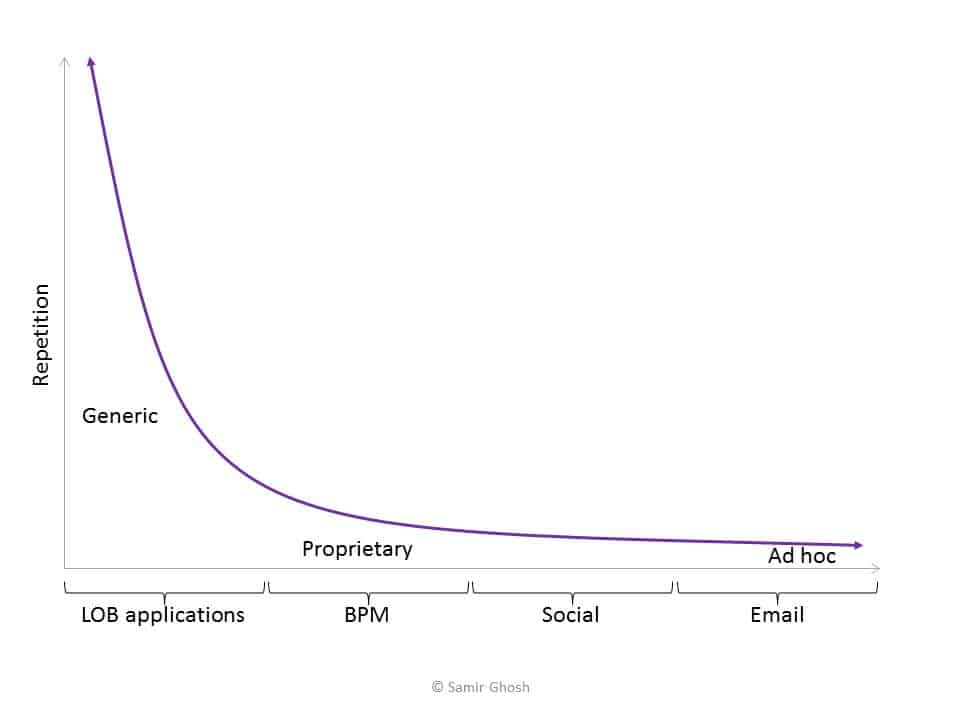
Within a business, the collective processes can be viewed as a spectrum. The more repetitive, team-oriented and generic, the more likely there will be a packaged line of business (LOB) application, like CRM, ERP, etc. More proprietary processes, those linked to the business’s competitive advantage, will likely need BPM solutions or custom applications. However, if a proprietary process is not highly repeatable, or does not involve many people, individuals tend to choose the tools used – email, spreadsheets, chat, etc.
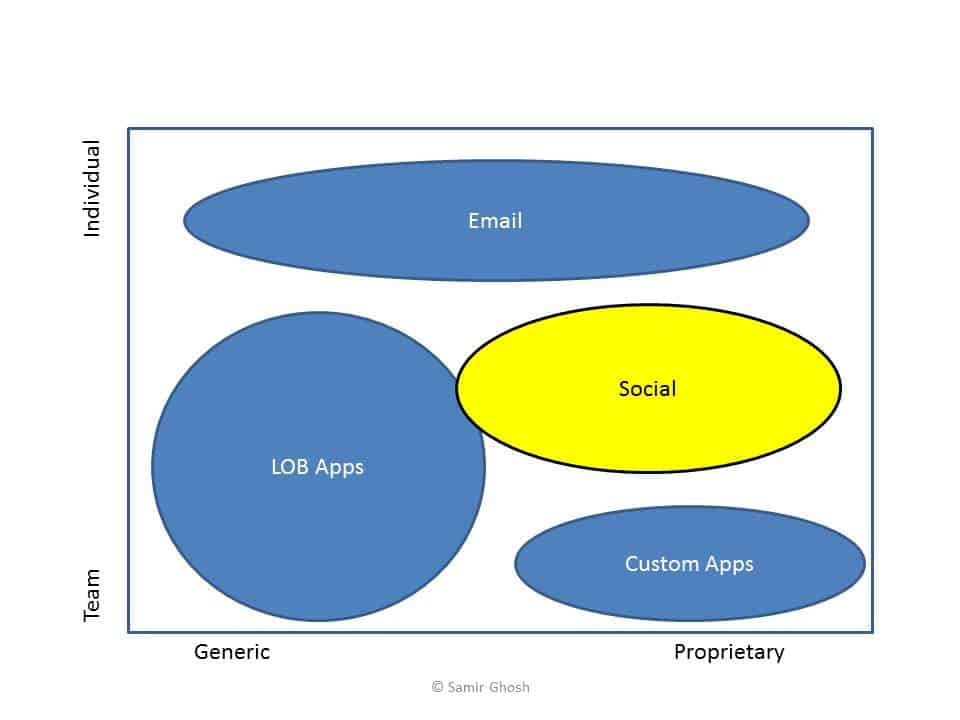
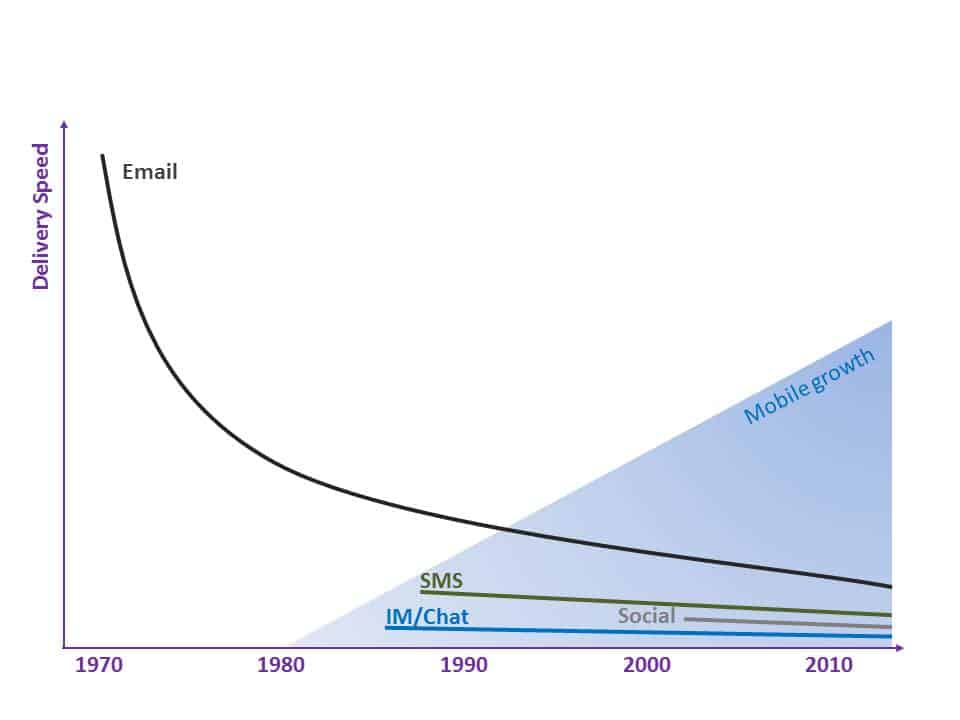
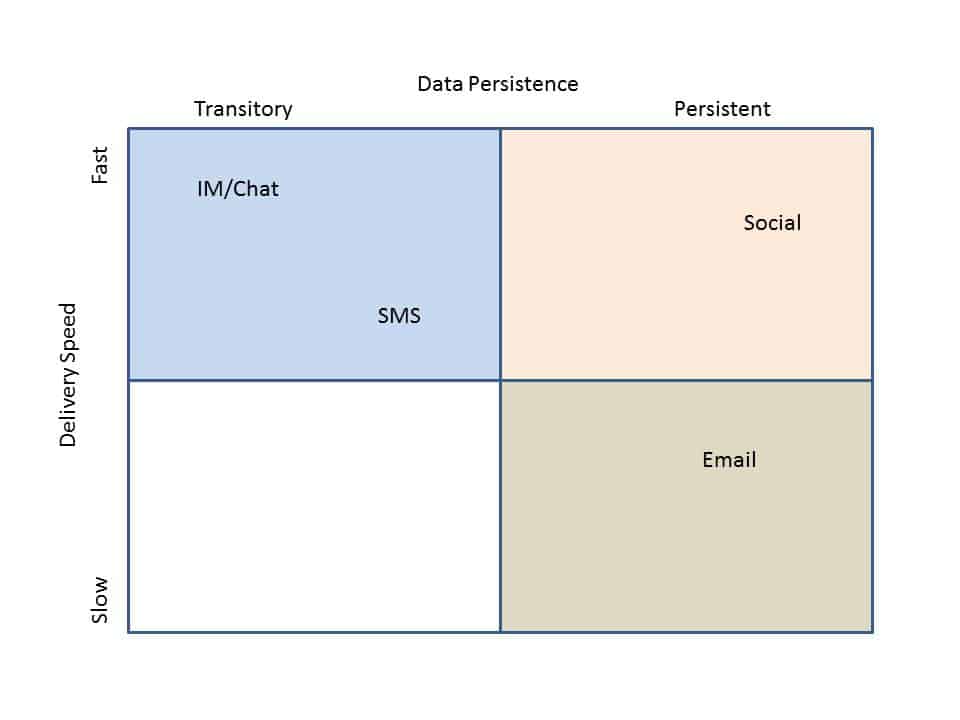
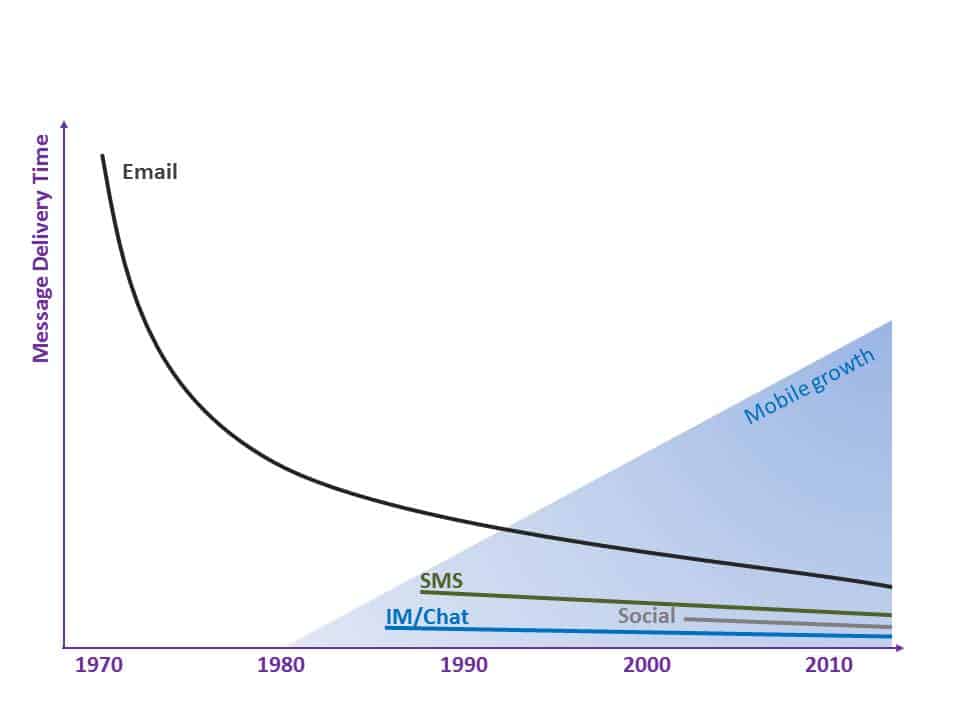
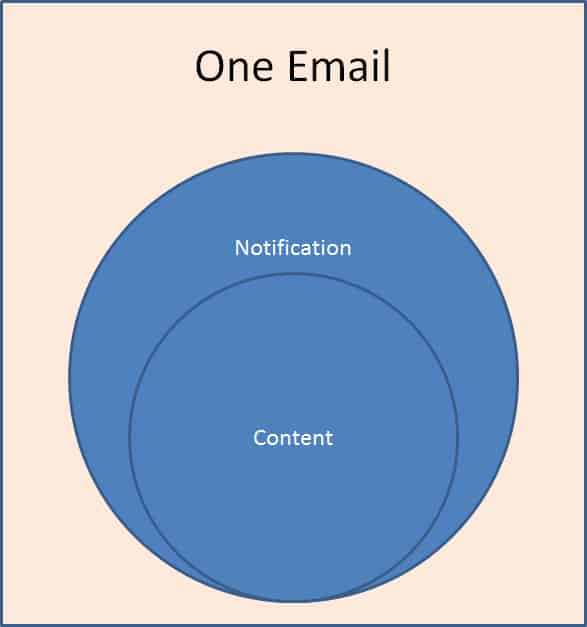
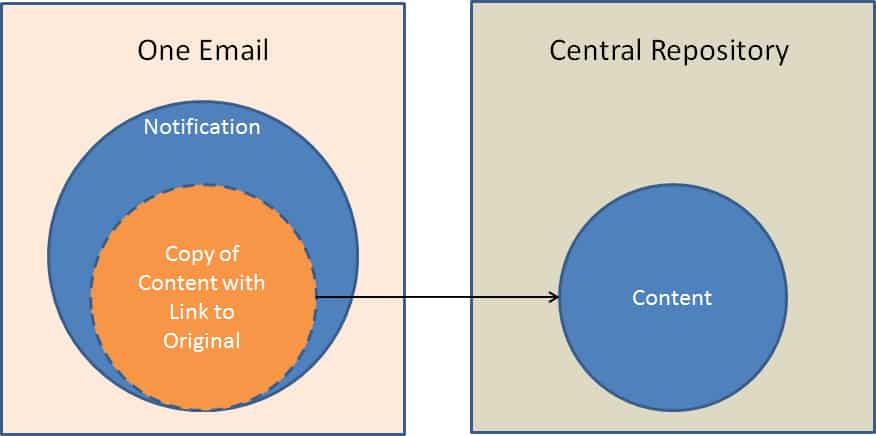
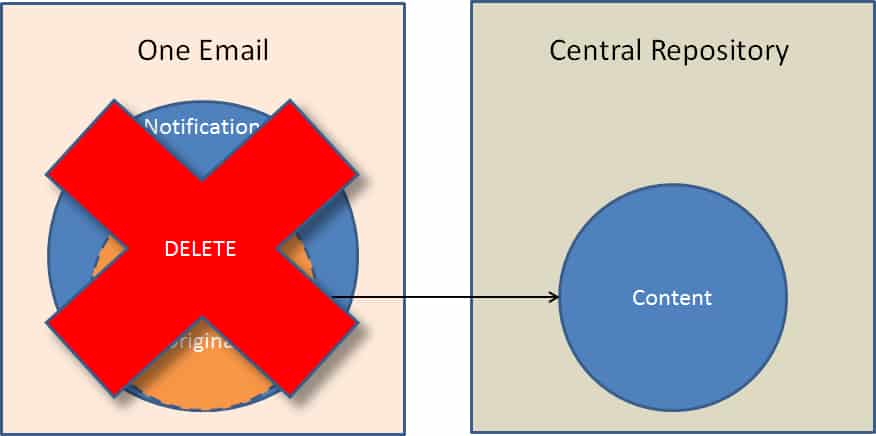
Social Collaboration fills the gap where processes are too proprietary and ad hoc (different enough each time) to warrant a custom or BPM solution, but also too collaborative or team-oriented for email to be an efficient solution.
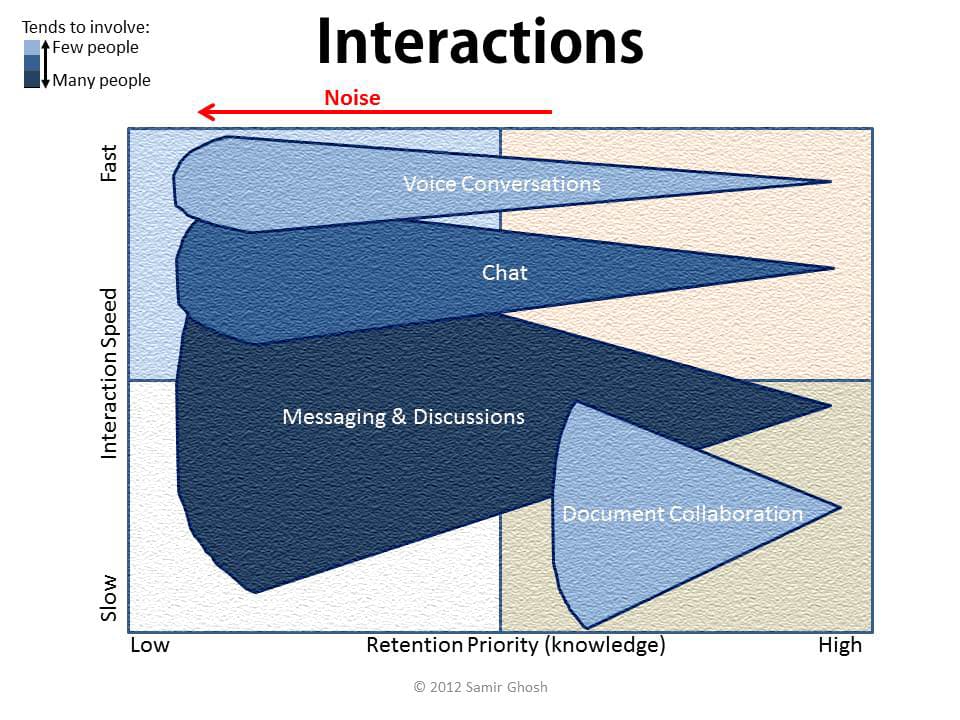
By leveraging Social Collaboration, these important “long-tail” processes can be also tamed by capturing and sharing learnings, providing transparency for broader contributions, enabling faster responses via self-subscription activity notifications, etc. These benefits are lost when relying on email, chat, phone and meetings to fill this gap alone.